Cardiovascular imaging and noninvasive testing give us a safe, accurate way to check your heart health. These safe, painless tests help us detect, diagnose and manage heart conditions like heart disease and heart failure.
Enhancing heart care with advanced cardiovascular imaging and noninvasive tests
Cardiovascular imaging and noninvasive testing give us a clear, detailed look at your heart. Using advanced tests like cardiac MRI, echocardiogram, EKG, cardiac CT and nuclear imaging, we can diagnose heart disease, find the cause of symptoms and monitor treatment for heart failure and other conditions. These tests help detect issues early, guide personalized care and track progress over time—supporting your heart health at every step.
Conditions
We use advanced heart imaging technology to provide accurate answers and personalized care. We can detect and diagnose a wide range of cardiovascular conditions, including:
- Aortic stenosis
- Arrhythmia
- Atrial fibrillation
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defects
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart failure
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Valvular heart disease
If your primary care doctor or cardiologist believes you have a condition affecting your heart or blood vessels, we encourage you to ask how Tufts Medicine’s expert cardiac radiology team and advanced heart imaging techniques can support your heart care journey.
Testing
You can trust that our doctors and care team will do everything they can to quickly, efficiently and accurately diagnose heart conditions. We’ll choose the right heart imaging tests for you based on your symptoms, medical history and family health history to make sure you get the best care.
A cardiac MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create images of your heart and the inside of your blood vessels. These images allow us to look for any potential conditions that can harm your heart health.
Because a cardiac MRI uses a strong magnet to create images, your care team will explain how to prepare for your MRI with steps like removing all metal objects beforehand. It’s important to note that people with some types of pacemakers or implanted defibrillators cannot undergo an MRI because the magnet can tamper with the devices. People with titanium implants (such as hip or knee replacements and most prosthetic heart valves and heart stents) are typically approved for an MRI.
For most cardiac MRI tests, your technician will inject you with a special type of dye called a contrast agent that helps light up specific tissues on the scan to detect scarring or other abnormalities of your heart muscle.
A CT scan uses specialized X-rays to diagnose conditions throughout your body, and they’re effective at visualizing your heart, too. A CT scan can help us evaluate blood vessels and coronary arteries for any signs of blockages or narrowing. Your doctor may give you a special dye called a contrast agent that helps provide us with detailed information about the blood vessels in your heart. Please note there is some radiation exposure with CT scans, but the benefits of accurate diagnosis and detailed imaging outweigh the minimal risk.
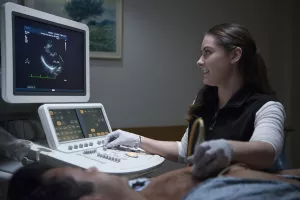
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of your heart. We use echocardiograms to answer important questions, like:
- Are your heart valves leaking or have restricted opening?
- Is your heart muscle thick?
- Is your heart pumping in a healthy way?
This test is performed by gliding a small hand-held wand (known as a transducer) across your skin. The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that travel until they hit a boundary, like your heart muscle and valves, and create an echo. When the echoes return to the transducer, they produce images on the ultrasound monitor in real-time.
A stress echocardiogram is a test that checks how your heart works when it’s put under stress. The test is broken down into 2 parts:
- Looking at the heart by using an electrocardiogram (EKG) and echocardiogram (echo)
- Stressing the heart by exercising or using chemicals
There are different types of stress echocardiograms:
- Exercise stress echocardiogram: Also known as the more traditional approach, this involves running on a treadmill while attached to an EKG.
- Chemical stress test: When running on a treadmill isn't a safe option, we use medications to artificially stress the heart.
It’s important to understand how your heart rate responds to exercise and rest. Exercise stress echocardiograms are special tests that allow your doctor to decipher whether you develop heart abnormalities when your heart rate increases during daily physical activities, like walking up stairs.
What to expect during an exercise stress echocardiogram
A care team member will be by your side the entire exam, monitoring your blood pressure and electrocardiogram (EKG) as you exercise. You’ll start by walking on the treadmill at a moderately slow pace. The treadmill will increase speed and tilt upward like a small hill every few minutes. We’ll monitor how you’re feeling throughout the test by asking questions like:
- Are you short of breath?
- Do you feel faint or dizzy?
- Do you have any chest pain?
Once you reach your maximum level of exercise, you’ll lie down on your left side on a nearby bed so the specialist captures additional cardiac imaging to provide clear, detailed insights into your heart health.
How to prepare for an exercise stress echocardiogram
Your cardiac care team will walk you through how to prepare for an exercise echocardiogram with instructions like:
- Not eating or drinking for 4 hours before the test
- Your doctor will determine whether you should temporarily stop taking any heart
- medications on the day of your test to see how your heart functions without the influence of medication
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing and sneakers
An electrocardiogram (EKG) is a test that checks your heart’s electrical activity. It’s used to diagnose conditions like heart failure, cardiac sarcoidosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, to name a few.
An EKG records the electrical signals as they travel through your heart, and interprets your heart beat and rhythm into a graph that your care team will examine.
Nuclear cardiac imaging is a type of nuclear medicine that uses small amounts of a safe radioactive substance to take pictures of your heart. These images help us see if some parts of your heart aren’t getting enough blood or aren’t working as they should. The test is often done with a stress test, where you either walk on a treadmill or take a medicine that makes your heart react like you’re exercising. This helps show how well blood is flowing to your heart. The amount of radiation is low, and the test is generally safe, with the benefits usually outweighing any risks.
How to prepare for a nuclear cardiac imaging stress test
Your cardiac care team will walk you through how to prepare for your nuclear medicine stress test with guidance such as:
- Ask your doctor about which medications you should take on the day of the test
- Wear light clothes and comfortable shoes since you’ll be exercising on a treadmill
- Only eat a light breakfast for a morning test or a light lunch for an afternoon test
- Please don’t consume any caffeine on the day of the test
Treatments
The power of cardiovascular imaging goes beyond diagnosing conditions. At Tufts Medicine, we’re leaders in using cardiac ultrasounds and other advanced imaging techniques to guide treatments and procedures. This helps ensure precise care and better outcomes. Our team uses these tools for a variety of procedures, including:
- Alcohol septal ablation for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
- Atrial septal defect (ASD) device closure
- Patent foramen ovale (PFO) device closure
- Surgical valve replacement
- Transcatheter valve replacement (TAVR)
- Transcatheter mitral valve repair
By using the latest imaging technology, we ensure that these procedures are performed with the highest level of accuracy and care.
Interventional radiology
Interventional radiology for cardiovascular care uses advanced imaging tools like CT scans, MRIs, ultrasounds and X-rays to guide us in performing heart and blood vessel procedures. We recommend these less invasive treatments for conditions like blocked arteries or heart valve problems. These procedures offer quicker recovery, less pain and fewer risks compared to traditional surgery, helping us return to our daily lives sooner.
From regular office visits to inpatient stays, find the healthcare you need and deserve close to home.

Meet the doctors and care team devoted to supporting you every step of the way along your path to better health.